EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
SCIENCE BIOLOGY (CHAPTER-16)
DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
______________________________________
1. Choose the correct answer among the following:
(a) Gastric juice contains
(i) pepsin, lipase and rennin
(ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin
(iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase
(iv) trypsin, pepsin and rennin.
(b) Succus entericus is the name given to
(i) a junction between ileum and large intestine
(ii) intestinal juice
(iii) swelling in the gut
(iv) appendix.
Solution: (a) (i) Pepsin, lipase and rennin
(b) (ii) Intestinal juice
2. Match column I with column II.
Column I Column II
(a) Bilirubin and (i)Parotid biliverdin
(b) Hydrolysis of (ii)Bile starch
(c) Digestion of fat (iii)Lipases
(d) Salivary gland (iv) Amylases
Solution: (a), – (ii),- (b) – (iv), (c) – (iii),- (d) – (i)
3. Answer briefly:
(a) Why are villi present in the intestine and not in the stomach?
(b) How does pepsinogen change into its active form ?
(c) What are the basic layers of the wall of alimentary canal?
(d) How does bile help in the digestion of fats ?
Solution: (a) The absorptive surface area of small intestine is enormously increased by microvilli and as maximum absorption
of digested food takes place in small intestine as compared to other organs, therefore, villi are present in small intestine and not in stomach. Moreover, stomach is primarily associated with temporary storage of food.
(b) The proenzyme pepsinogen, on exposure to hydrochloric acid, secreted by oxyntic cells of gastric glands gets converted into the active enzyme pepsin, the proteolytic enzyme of the stomach.
(c) The wall of alimentary canal from oesophagus to rectum possesses four layers, namely serosa, muscularis, sub-mucosa and mucosa. Serosa is the outermost layer and is made up of a thin mesothelium with some connective tissues. Muscularis is formed by smooth muscles. The sub-mucosal layer is formed of loose connective tissues containing nerves, blood and lymph vessels. In duodenum, glands are also present in sub-mucosa. The innermost layer lining the lumen of the alimentary canal is the mucosa. This layer forms irregular folds (rugae) in the stomach and small finger¬like foldings called villi in the small intestine.
(d) Bile has no enzymes but contains bile salts, namely, sodium bicarbonate, sodium glycocholate and sodium taurocholate that reduce the surface tension of large fat droplets and break them into many small droplets by a process known as emulsification. These small fat droplets present large surface area for lipase (fat digesting enzyme) to act upon them. Moreover, bile also activates lipases.
4. State the role of pancreatic juice in digestion of proteins.
Solution: The pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes – trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases. Trypsinogen is acti¬vated by an enzyme enterokinase, (secreted by the intestinal mucosa) into active trypsin, which in turn activates the other enzymes of the pancreatic juice. Proteins, proteoses and peptones (partially hydrolysed proteins) in the chyme reaching the intestine are acted upon by these proteolytic enzymes of pancre¬atic juice.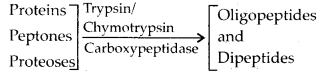
5. Describe the process of digestion of protein in stomach.
Solution: The gastric glands of the stomach secrete gastric juice that contains HCl and proenzymes – pepsinogen and prorennin. The proenzyme pepsinogen, on exposure to HCl gets converted into the active enzyme pepsin, the proteolytic enzyme of stomach. The pepsin converts proteins into proteoses and peptones (peptides). Prorennin is found in gastric juice of infants and is activated by pepsin into active rennin. It helps in digestion of milk protein casein.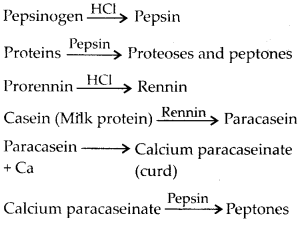
6. Give the dental formula of human beings.
Solution: The dental formula of human beings is![]()
It shows arrangement of teeth in each half of
the upper and lower jaw.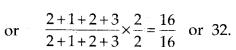
7. Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. Why ?
Solution: Bile has no enzymes but contains bile salts, namely, sodium bicarbonate, sodium glycocholate and sodium taurocholate that reduce the surface tension of large fat drop¬lets and break them into many small droplets by a process known as emulsification. These small fat droplets present large surface area for lipase (fat digesting enzyme) to act upon them. Moreover, bile also activates lipases.![]()
8. Describe the digestive role of chymotrypsin. Which two other digestive enzymes of the same category are secreted by its source gland ?
Solution: Chymotrypsin is a proteolytic enzyme of pancreatic juice secreted by exocrine part of pancreas. It helps in digestion of proteins. It converts proteins, peptones and proteoses into oligopeptides and dipeptides. Two other proteolytic enzymes present in pancreatic juice are trypsinogen and procarboxypeptidase.
9. How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested ?
Solution: Digestion of polysaccharides (starch and glycogen) starts from buccal cavity. In buccal cavity, polysaccharides are acted upon by salivary amylase or ptyalin which splits starch and glycogen into disaccharides and small dextrins called ‘a’ dextrin.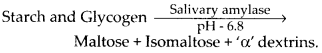
The digestion of carbohydrates does not occur in stomach because gastric juice itself has no carbohydrase.
In small intestine, the food mixes with two juices, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice. Pancreatic juice contains a carbohydrase named pancreatic amylase. This enzyme hydrolyses more starch and glycogen.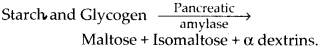
Intestinal juice contains carbohydrases; maltase, isomaltase, a-dextrinase, sucrase and lactase which act on disaccharides as follows: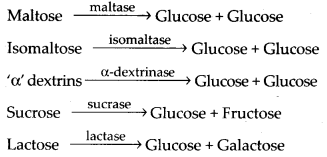
fructose and galactose are monomers of carbohydrates. These are absorbed by intestinal mucosa.
10. What would happen if HCl were not secreted in the stomach?
Solution: HCl is secreted by parietal or oxyntic cells of gastric glands. It serves the following functions:
- It activates the pepsinogen and prorennin into their active form pepsin and rennin.
- It provides the acidic pH (pH 1.8) optimal for pepsin.
- It kills the harmful bacteria present in the food.
- It stops the action of saliva on food. Pepsin and rennin are the principle proteolytic enzymes of stomach. If these enzymes are not activated by HCl then digestion of protein will not take place in stomach, and also the harmful bacteria can cause various diseases.
11. How does butter in your food get digested and absorbed in the body ?
Solution: Butter is a saturated fat. Fats and oils of the ingested food are triglycerides.
They are digested by lipases. Small intestine is the principal organ for fat digestion.
In the small intestine food meets three secretions, bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice, all alkaline in nature.
Bile contains no enzyme but it contains bile salts which reduces the surface tension of large fat droplets and breaks them into smaller ones (emulsification).![]()
Emulsified triglycerides Pancreatic juice contains pancreatic lipase, which is the principal fat digesting enzyme. It is activated by bile.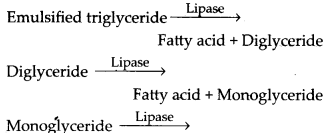
Fatty acid + Glycerol Intestinal lipase found in intestinal juice hydrolyses some triglycerides, diglycerides and monoglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol like pancreatic lipase.
Fatty acids, glycerol and monoglycerides are the end products of fat digestion and being insoluble in water cannot be directly absorbed from the intestinal contents. So they combine with the bile salts and phospholipids to form micelles (water soluble). From the micelles fatty acids, glycerides, sterols and fat soluble vitamins are absorbed into the intestinal cells by diffusion where they are resynthesised in the ER and are converted into very small protein coated fat molecules (droplets) called chylomicrons. The latter are released from the intestinal cells into the lymph present in the lymphatic capillaries, the lacteals. These lacteals ultimately release the absorbed substances into the blood stream.
12. Discuss the main steps in the digestion of proteins as the food passes through different parts of the alimentary canal.
Solution: Proteins of ingested food are broken down into amino acids by proteases (peptidases). Proteases are secreted in inactive forms called proenzymes which are converted into active forms at site of their action. Protein digestion starts in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. Saliva contains no protease.
Digestion of proteins in stomach : Chief cells of gastric gland secrete pepsinogen and prorennin, which act as follows: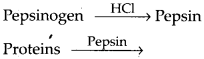
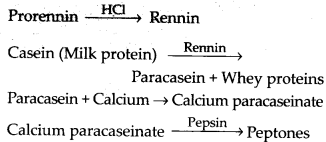
Digestion of proteins in small intestine: In small intestine, peptones and proteoses are acted upon by enzymes of pancreatic juice and intestinal juice.
Pancreatic juice contains 3 inactive proteases; trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and pro-carboxypeptidase. Their action is as follows: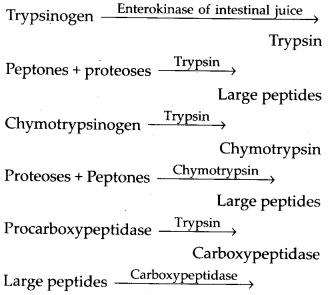
Dipeptides + Amino acids Intestinal juice contains two digestive pro-teases; aminopeptidases and dipeptidases and a nondigestive enterokinase (enteropep- tidase).
Amino acids are the end products of protein digestion which are absorbed by intestinal cells.
13. Explain the term thecodont and diphyodont.
Solution: Thecodont: In human, each tooth is embedded in a socket of jaw bone. Such teeth are described as thecodont.
Diphyodont: Majority of mammals including human beings form two sets of teeth during their life, a set of temporary milk or deciduous teeth replaced by a set of permanent or adult teeth. This type of dentition is called diphyodont.
14. Name different types of teeth and their number in an adult human.
Solution: Adult human has 32 teeth with the![]()
Human has heterodont dentition i.e., having four different types of teeth. The number of different types of teeth in human are as follows:incisors = 8, canines = 4, premolars = 8, molars = 12
15. What are the functions of liver?
Solution: Liver is the largest gland of the body and consists of hepatic cells. Besides being a digestive gland, the liver performs a number of functions for the welfare of body. Its varied functions are as follows
- Secretion of bile.
- Glycogenesis, gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis.
- Storage of fat, glycogen, vitamins like A, D, E, K and B12, blood, water, etc.
- Deamination of amino acids.
- Synthesis of urea.
- Elimination of excretory substances.
- Detoxification of harmful substances.
- Formation and breakdown of blood
corpuscles, i.e., in embryos, liver is haemopoietic (produces red blood corpuscles) and in adults its Kupffer cells phagocytise and destroy worn out and dead RBCs. - Secretion of blood proteins, i.e., prothrombin and fibrinogen.
- Secretion of anticoagulant heparin.
- Production of heat.
- Secretion of enzymes.