EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
09/11/2021 CLASS- 10 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT : SCIENCE
CHAPTER-10
LIGHT REFLECTION & REFRACTION
______________________________________
Question 1 Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens ?
(a) Water
(b) Glass
(c) Plastic
(d) Clay
Answer:
(d) Clay
Question 2 The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object ?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Answer:
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Question 3 Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens (b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
Answer:
(b) At twice the focal length.
Question 4 A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be :
(a) Both concave.
(b) Both convex.
(c) the mirror is concave and the lens is convex.
(d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave.
Answer:
(a) Both concave
Question 5 No matter how far you stand from mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) plane
(b) concave
(c) convex
(d) either plane or convex.
Answer:
(d) Either plane or convex.
Question 6 Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary ?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm.
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm.
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm.
Answer:
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
Question 7 We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror ? What is the nature of the image ? Is the image larger or smaller than the object ? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer:
A concave mirror gives an erect image when the object is placed between the focus F and the pole P of the concave mirror, i.e., between 0 and 15 cm from the mirror. The image thus formed will be virtual, erect and larger than the object.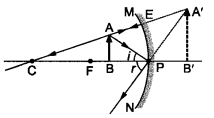
Question 8 Name the type of mirror used in the following situations.
(a) Headlights of a car.
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle.
(c) Solar furnace.
Support your answer with reason.
Answer:
(a) Concave mirrors are used as reflectors in headlights of cars. When a bulb is located at the focus of the concave mirror, the light rays after reflection from the mirror travel over a large distance as a parallel beam of high intensity.
(b) A convex mirror is used as a side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle because
- A convex mirror always forms an erect, virtual and diminished image of an object placed anywhere in front it.
- A convex mirror has a wider field of view than a plane mirror of the same size.
(c) Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Question 9 One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object ? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Answer:
A convex lens forms complete image of an object, even if its one half is covered with black paper. It can be explained by considering following two cases.
Case I : When the upper half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object will be refracted by the lower half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the following figure.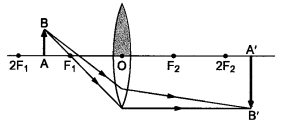
Case II: When the lower half of the lens Is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object is refracted by the upper half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the given figure.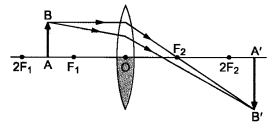
Question 10 An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Answer:
Here : Object distance, u= -25 cm,
Object height, h = 5 cm,
Focal length, f = +10 cm
According to the lens formula,
⇒
The positive value of v shows that the image is formed at the other side of the lens.
The negative value of image height indicates that the image formed is inverted.
The position, size, and nature of image are shown alongside in the ray diagram.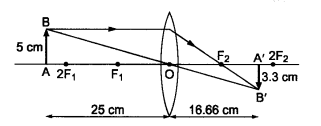
Question 11
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens ? Draw the ray diagram.
Solution:
Focal length, f = -15 cm, Image distance, ν = -10 cm (as concave lens forms the image on the same side of the lens)
From the lens formula 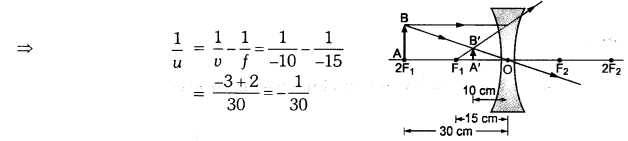
Object distance, u = -30 cm
The negative value of u indicates that the object is placed in front of the lens.
Question 12
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
Solution:
Object distance, u = -10 cm, Focal length, f = +15 cm, Image distance, ν = ?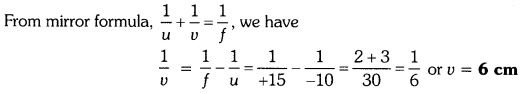
Thus, image distance, ν = + 6 cm
Because ν is +ve, so a virtual image is formed at a distance of 6 cm behind the mirror.
Magnification,
The positive value of m shows that image erect and its value, which is less than 1, shows that image is smaller than the object. Thus, image is virtual, erect and diminished.