EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
13/10/2021 CLASS-8 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT :SOCIAL SCIENCE
chapter - 3
MINERAL AND POWER RESOURCES
______________________________________
Question 1.Choose the correct option.
(i) Which of these is a non-metallic mineral?
(a) Iron ore
(b) Bauxite
(c) Limestone
(d) Manganese ore
(ii) Which continent produces more than half of the world’s tin?
(a) Africa
(b) Asia
(c) Europe
(d) South America
(iii) Which continent is the leading producer of iron ore in the world?
(a) North America
(b) Asia
(c) Europe
(d) Australia
(iv) Which state is a major bauxite producing area?
(a) Goa
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Assam
(d) Tamil Nadu
(v) What is the name given to the electricity produced from coal?
(a) Nuclear power
(b) Thermal power
(c) Fossil fuel
(d) None of these
(vi) Which of these is a conventional source?
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Natural gas
(d) All of these
(vii) Which of these is called buried sunshine?
(a) Petroleum
(b) Coal
(c) Solar energy
(d) Tidal energy
Answer:
(i) (c), (ii) (b), (iii) (c), (iv) (b), (v) (b), (vi) (d), (vii) (b).
Question 2.Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- Metallic minerals are classified into …………….. and ………….
- Gold and silver are …………. minerals.
- Minerals can be extracted by ………….,…………., or …………
- Deep bores dug to reach mineral deposits are called …………
- Metallic minerals are generally found in ……….. and…………..rock formations.
- The mineral deposits in North America have located in three zones: …………… the Appalachian region and the mountain ranges of the West.
- …………… is the largest producer of bauxite in the world.
- …………. is the most abundantly available fossil fuel.
- Petroleum is drilled from ………
- Bhakra Nangal is an important …………….. station in India.
- …………… and……… are radioactive metals.
Answer:
- ferrous, non-ferrous
- non-ferrous
- mining, drilling, quarrying
- shafts
- igneous, metamorphic
- the Canadian region north of the Great Lakes
- Australia
- Coal
- Oil fields
- hydel power
- Uranium, thorium.
Question 3.State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- All ores are rocks but all rocks are not minerals.
- Quarrying is good for the environment.
- Mineral fuels like coal and petroleum are found in sedimentary strata.
- Coal is more predominant in the Canadian Shield Region than the Appalachians.
- Chile and Peru are leading producers of copper.
- Kolar in Karnataka has large deposits of silver.
- Copper is an element used in almost everything.
- Bauxite is the ore of aluminium.
- Nuclear power can be produced from the nuclei of most elements.
Answer:
- Ture
- False
- Ture
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
Question 4. Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II.
Answer:
(i) (d), (ii) (a), (iii) (b), (iv) (c), (v) (e).
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between a rock and an ore.
Answer:
A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals. An ore is a rock from which minerals are mined.
Question 2.
Define quarrying.
Answer:
Quarrying is a process of extraction in which minerals lying near the surface are simply dugout.
Question 3.
Name the leading tin producers in Asia.
Answer:
China, Malaysia, and Indonesia are leading tin producers in Asia.
Question 4.
Name two areas in Australia, which have large deposits of gold.
Answer:
Two areas in Western Australia having large deposits of gold are Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie.
Question 5.
Name two minerals in whose production India contributes a significant part.
Answer:
India has vast deposits of high-grade iron ore, and it is also a leading producer of salt.
Question 6.
In which industry is silicon important? From which ore is it obtained?
Answer:
Silicon is important in the computer industry. It is obtained from quartz.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name and describe briefly methods of extraction.
Answer:
Mining, drilling, and quarrying are methods of extraction. Mining is a process of extraction of taking out minerals from rocks under the earth’s surface.
- Opencast mining: In this, minerals lying at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer.
- Shaft mining: In this, deep bores (called shafts) are made to reach mineral deposits lying at large depths.
- Drilling: In this, deep wells are bored to take out minerals.
- Quarrying: It is the process of extraction in which minerals lying very close to the surface are extracted just by digging them out.
Question 2.
Where are minerals found?
Answer:
Minerals are found in different types of rocks. Metallic minerals are usually found in igneous and metamorphic rocks that form large plateaus. Examples: iron ore is found in north Sweden, copper, and nickel in Canada. In igneous and metamorphic rocks in South Africa, iron, nickel, chromites, and platinum are found. Non-metallic minerals are found in sedimentary rock formations. Limestone deposits are found in France. Mineral fuels such as coal and petroleum are found in sedimentary strata.
Question 3.
Describe the mineral distribution in North America.
Answer:
The mineral deposits in North America are found in three zones: the Canadian region in the north of the Great Lakes, the Appalachian region, and the Rocky Mountains in the West. Iron ore, nickel, gold, uranium, and copper are mined in the Canadian Shield Region, coal in the Appalachian region. Western Cordilleras have vast deposits of copper, lead, zinc, gold, and silver.
Question 4.
Write common uses of minerals.
Answer:
Minerals are important in many industries. Minerals used in gems are usually very hard. These are then set in varying styles of jewellery. Iron and copper are metals used in almost everything. Copper is present in everything from coins to pipes and electricity wires. Silicon, obtained from the mineral quartz, is the base of the computer industry. Aluminium, obtained from bauxite ore, and its alloys are used in aeroplanes due to their lightweight. Aluminium is also used in kitchen cookware.
Question 5.
How is hydroelectricity, produced?
Answer:
Hydroelectricity is produced from the energy possessed by water falling from great heights. River water is stored in dams. When rainwater or river waterfalls from heights, it flows over turbine blades placed at the bottom of the dam. The moving blades are connected to a generator which produces electricity from this energy. This electricity is called hydroelectricity. The water discharged after its production is used for irrigation.
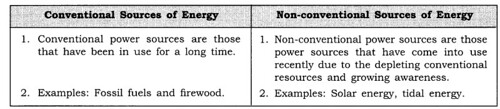
Question 4.
Distinguish between the following.
(i) Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
(ii) Biogas and natural gas.
(iii) Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
(iv) Metallic and non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
(i)