EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
SCIENCE (CHAPTER-5)
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE
______________________________________
Question 1. Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer: Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665 while examining a thin slice of cork through a self-designed microscope. He saw that the cork resembled the structure of a honey comb consisting of many little compartments. These small boxes are called cells.
Question 2. Why the cell is called the structural and Junctional unit of life?
Answer: A cell is capable of independently carrying out all necessary activities of life. So, they are called basic or functional unit of life.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 61
Question 1. How do substances like C02 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer: CO2 moves by diffusion and H2O move by osmosis through cell membrane.
Question 2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer: It is called selectively permeable membrane because it allows the entry and exit of some substances, not all.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 63
Question 1. Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 65
Question 1. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer: The two organelles which have their own genetic material are:
1. Mitochondria 2. Plastids
Question 2. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer: The cell will not be able to revive and lysosomes will digest it.
Question 3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide hags?
Answer: When the cell gets damaged, lysosomes may burst, and the enzymes digest their own cell. Therefore lysosomes are known as suicide bags.
Question 4. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer: The proteins are synthesised in the ribosomes that are also known as protein factories.
Questions From NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science
Question 1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are also different from animal cells.
Answer:
Question 2. How is prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer: Prokaryotic cell is generally smaller in size (1-10 pm), nuclear region is poorly defined, the cell organelles are not membrane-bound and has a single chromosome.
Eukaryotic cell is generally larger in size (5-100 pm), nuclear region is well defined with nuclear membrane. Membrane-bound cell organelles are present and has more than one chromosome.
Question 3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer: If plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down then molecules of some substances will freely move in and out.
Question 4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer: Golgi apparatus has the function of storage, modification and packaging of the products in vesicles. If there were no Golgi bodies, packaging and dispatching of materials synthesised by the cell will be stocked.
Question 5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer: Mitochondria is known as powerhouse of the cell because it releases the energy required for different activities of life.
Question 6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer: Lipids and proteins are synthesised in ER [Endoplasmic Reticulum].
Question 7. How does Amoeba obtain it’s food?
Answer: Amoeba take it’s food by the cell membrane which forms the food vacuole.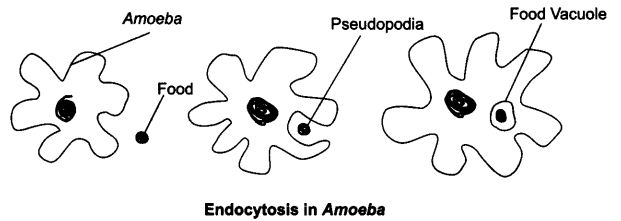
Question 8. What is osmosis?
Answer: Osmosis is the process of movement of water molecule from a region of higher water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane to a region of lower water concentration.

