EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
Monday, October 25, 2021
CLASS-NURSERY SUBJECT-ENGLISH REVISION QUESTIONS FIRST TERM EXAMINATION
25/10/2021 CLASS-NURSERY SESSION 2021-22
FIRST TERM EXAMINATION
Monday, October 18, 2021
CLASS-10 SCIENCE CHAPTER-7 CONTROL AND CO-ORDINATION
EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
18/10/2021 CLASS-10 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT :SCIENCE
chapter - 7
CONTROL AND CO-ORDINATION
______________________________________
Question 1 Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin
Answer:
(d) Cytokinin
Question 2 The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite
(b) synapse
(c) axon
(d) impulse
Answer:
(b) Synapse
Question 3 The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking
(b) regulating the heart beat
(c) balancing the body
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(b) All of the above
Question 4 What is the function of receptors in our body ? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise ? [AICBSE 2016]
Answer:
Receptors are specialised cells located in our sense organs like ear, nose, skin, tongue and eyes. The function of receptors is to detect information from the environment. For example, olfactory receptors detect smell. If receptors do not work properly, the information obtained from the environment will be delayed to reach the spinal cord or brain. In this situation, the response to the environmental stimulus will be delayed causing harm to the body. For example, if skin receptors are damaged, and one accidentally touches a hot object, then his/her hands might get burn as the damaged receptor cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
Question 5 Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function. [AICBSE 2017]
Answer:
Nerve cell or neuron is the functional unit of nervous system. A nerve cell has three parts-
(i) cell body
(ii) dendrite
(iii) axon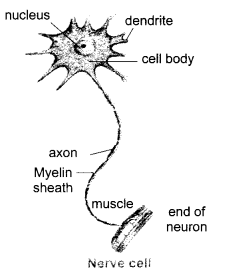
Function : The function of nerve cells is to carry information in the form of electrical signals which are called nerve impulses. Cells receive stimulus to send it to spinal cord and brain and carry the message from brain to the target organ.
Question 6 How does phototropism occur in plants ?
Answer:
The movement in any part of a plant due to light is called phototropism. The shoot of plant shows positive phototropism and roots show negative phototropism.
Phototropism in plants occurs due to the hormone auxin. When light falls on one side of a plant, the secretion of auxin hormone is more in the part away from the light. Hence, auxin causes growth in length of the cells in shady part. So, the plant appears to bend towards light.
Question 7 Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury ?
Answer:
(i) All the involuntary actions will get disturbed.
(ii) Reflex actions will be disturbed because reflexes are located in the spinal cord. Therefore, the quick responses required to safe guard the body will not take place.
Question 8 How does chemical coordination occur in plants ?
Answer:
Chemical coordination in plants takes place with the help of plant hormones. In most of the regions where division takes place (meristematic regions) stimuli cells secrete chemical compounds (hormone). These substances identify the information by stimulating the other nearby cells and communicating the information.
Question 9 What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism ?
Answer:
An organism needs control and coordination system for the following functions :
(i) To save the body of the organisms from the harmful changes in the environment.
(ii) To control the speed of voluntary and involuntary actions.
(iii) To have the capability to think and learn for responding to any stimuli.
Question 10 How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other ?
Answer:
| Involuntary actions | Reflex actions |
| 1. Those actions which occur immediately without any thinking are called involuntary actions. | 1. Reflex action is an immediate response to an event which does not require any processing by brain. |
| 2. Involuntary actions are controlled by mid and hind brain. Example: Breathing, beating of heart, etc. | 2. Reflex actions are controlled by spinal cord. Example: Sneezing, coughing, etc. |
Question 11 Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
| Nervous mechanism | Hormonal mechanism |
| It is a fast process. | It is a slow process. |
| Arteries and glands are affected. | It affects the target organ. |
| It transmits in electrochemical form. | It transmits in chemical form. |
| It does not control metabolism. | It controls metabolism. |
| Growth is not affected. | Growth is affected. |
Question 12 What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs ?
Answer:
| Movement in a sensitive (mimosa) plant | Movement in legs of a human |
| 1. The leaves of a sensitive plant like mimosa are sensitive to touch. | 1. Leg is in control of nerve muscles. |
| 2. It is not controlled by any part of the plant. | 2. It is controlled by brain and spinal cord. |
| 3. In this, cells change their shape on changing the amount of water in them. | 3. Amount of water has no effect on the movement of muscles. |
| changing the amount of water in them. | the movement of muscles. |
| 4. The movement in a sensitive plant are nastic movement. | 4. The movement in our leg is due to voluntary nervous system. |
Control and Coordination Class 10 HOTS
Question 1. What type of plant movement is seen in the diagram of coiling of tendril?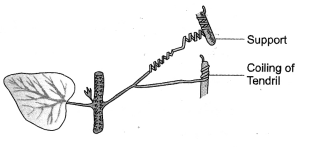
Or
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support? Describe in brief. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Thigmotropism or curvature movement that occurs in response to contact. Less auxin is present in the region of contact. The free side having more auxin shows more growth. This causes the tendril to coil over the support.
Question 2. Identify and label the parts shown as A and B in the accompanying figure.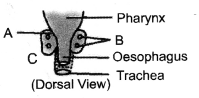
Answer:
Dorsal view of thyroid an parathyroid.
A – Thyroid,
B- Parathyroid.
Question 3. What are the hormones involved in providing milk to the suckling infant ?
Answer:
1. Prolactin (Maternity Hormone). Production of milk.
2. Oxytocin Ejection of milk.
Question 4. How does pancreas control glucose level of blood ?
Answer:
Pancreas produces two hormones
- Insulin from P-cells of islet of Langerhans and
- Glucagon from a- cells of islets of langerhans.
Insulin is produced when glucose level of blood rises. Insulin helps the cells to withdraw glucose from blood. It also converts glucose into glycogen in liver and muscles.
Question 5. Glucagon is secreted when glucose level of blood falls. It mobilises reserve food like glycogen into glucose. What is pregnancy hormone ? Why is it known so ?
Answer:
Progesterone is called pregnancy hormone. It helps in maintaining pregnancy by non-formation of new ova, promoting thickening and secretory activity of uterine wall and attachment of embryo to the uterine wall.
Question 6. What is dormin ?
Answer:
Dormin is the other name of plant hormone abscisic acid. The hormne induces dormancy in buds and seeds. So it has been called dormin.
Question 7. Name the parts labelled A and B in the neuron drawn above.
- Which part acquires the information in the neuron ?
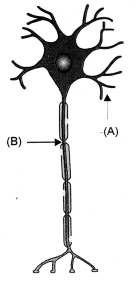
- Through which part does the information travel ?
- In what form does this information travel ?
- Where is the impulse converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission ?
(b) Name the hormone secreted by thyroid. What is the function ?
(c) Why is the use of iodised salt advisable ?
(CBSE A.I. 2008 Compt.)
Answer:
(a)
- A-Dendrite, B-Axon
- Dandrite.
- Dandrite to cell body or cyton to axon.
- Electrical impulse
- In the region of synapse.
Impulse stimulates the release of chemical neurotransmitter from the surface of presynaptic knob or bouton of axon terminal. Neurotransmitter (e.g. acetylcholine) comes in contact with chemoreceptor sites of post-synaptic membrane of the next neuron and generates a fresh impulse.
(b) Thyroxine:
Function of Thyroxine. It controls
- Basal metabolic rate
- Metabalism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
- Consumption of energy in physical activity and body temperature
- Development and differentiation.
(c) Iodised Salt: Salt is iodised to provide iodine to thyroid for synthesis of thyroxine which is iodine containing hormone.
Question 8.
(a) What are plant hormones ? Give one example each of a plant hormone that
- promotes growth
- inhibits growth.
- promotes cell division
- promotes the growth of a tendril around a support. (CCE 2011)
(b) Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram given below. Write one function of each part. (CBSE A.I. 2008 Comptt. Delhi 2008 Comptt.)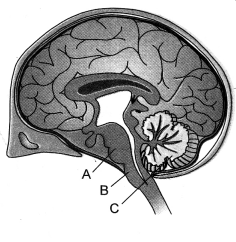
Answer:
(a) Plant Hormones:
Phytohormones are chemical substances other than nutrients produced naturally in plants which regulate growth, development, differentiation and a number of physiological processes, e.g., auxin, gibberellins, abscisic acid, cytokinins.
- Hormone That Promotes Growth. Auxin/Gibberellin.
- Hormone That Inhibits Growth. Abscisic acid or ABA
- Hormone That Promotes Cell Division. Cytokinin.
- Hormone That Promotes Growth of a Tendril Around a Support. Auxin.
(b) A-Pons Function: Relay centre, pneumotaxic area of respiratory centre.
B-Medulla Function: Reflex centre, cardiac centre, respiratory centre.
C-Cerebellum Function: Maintains equilibrium and coordinates muscular activities
Thursday, October 14, 2021
CLASS-9 SUBJECT -SCIENCE CHAPTER-15 IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCES,
EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
14/10/2021 CLASS-9 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT :SCIENCE
chapter - 15
IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCES
______________________________________
Page 204
Question 1. What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables?
Answer: Cereals give carbohydrates which provide energy.
Pulses give proteins which build our body.
Vegetables and fruits provide vitamins and minerals.
Page 205
Question 1. How do biotic and abiotic factors affect crop production?
Answer: Factors responsible for loss of grains, during storage and production are:
(a) Biotic factors like rodents, pests, insects, etc.
(b) Abiotic factors like temperature, humidity, moisture, etc.
Combination of both biotic and abiotic factors causes :
- infestation of insects
- weight loss
- poor germination ability
- degradation in quality
- discolouration
- poor market price
Question 2. What are the desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements?
Answer: Desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements are:
(a) Tallness and profuse branching are desirable characters for fodder crops.
(b) Dwarfness is desired in cereals, so that less nutrients are consumed by these crops.
Page 206
Question 1. What are macro-nutrients and why are they called macro-nutrients?
Answer: Macro-nutrients are the essential elements which are utilised by plants in large quantities. Many macro-nutrients are required by the plants for the following functions:
- As the constituent of protoplasm
- N, P, S are present in proteins
- Ca is present in cell wall
- Mg is important constituent of chlorophyll
Question 2. How do plants get nutrients?
Answer: Plants get nutrients from air, water and soil. There are, sixteen nutrients essential for the growth of plants. Carbon and Oxygen are supplied by water. The remaining thirteen nutrients are supplied by soil.
Page 207
Question 1. Compare the use of manure and fertilizers in maintaining soil fertility.
Answer: Effects of using manures on soil quality:
- The manures enrich the soil with nutrients.
- They provide a lot of organic matter (humus) to the soil and thus restores water retention capacity of sandy soils and drainage in clayey soil.
- The addition of manures reduces soil erosion.
- They provide food for soil organisms, like soil friendly bacteria.
Effects of using fertilizers on soil quality:
- By the continuous use of fertilizers, the soil becomes powdery, dry and rate of soil erosion increases.
- By the use of fertilizers, the organic matter decreases which further decreases the porosity of soil and the plant roots do not get oxygen properly,
- The nature of soil changes to acidic or basic.
Page 208
Question 1. Which of the following conditions will give the most benefits? Why?
(a) Farmers use high-quality seeds, do not adopt irrigation or use fertilizers.
(b) Farmers use ordinary seeds, adopt irrigation and use fertilizer.
(c) Farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures.
Answer: In this, (c) Farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures.
Use of any quality seeds is not sufficient until they are properly irrigated, enriched with fertilizers and protected from biotic factors. Hence, option (c) will give the most benefits.
Page 209
Question.1. Why should preventive measures and biological control methods be preferred for protecting crops?
Answer. Diseases in plants are caused by pathogens. To get rid of pathogens, some preventive measures and biological control methods are used as they are simple, economic and minimise pollution without affecting the soil quality.
Question 2. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Answer: The factors responsible for losses of grains during storage are:
- Abiotic factors like moisture (present in food grains), humidity (of air) and temperature.
- Biotic factors like insects, rodents, birds, mites, bacteria and fungi.
Page 210
Question 1. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why ?
Answer: Cross breeding is a process in which indigenous varities of cattle are crossed by exotic breeds to get a breed which is high yielding. During cross breeding, the desired characters are taken into consideration. The offspring should be high yielding, should have early maturity and should be resistant to climatic conditions.
Page 211
Question 1. Discuss the implications of the following statement:
“It is interesting to note that poultry is India’s most efficient converter of low fibre food stuff (which is unfit for human consumption) into highly nutritious animal protein food”.
Answer: The basic aim of poultry farming is to raise domestic fowl for egg production and chicken meat. These poultry birds are not only the efficient converters of agricultural by-products, particularly cheaper fibrous wastes (which is unfit for human consumption but can be formulated into cheaper diets for poultry birds) into high quality meat and also help in providing egg, feathers and nutrient rich manure. For this reasons, it is said that, “poultry is India’s most efficient converter of low fibre food stuff into highly nutritious animal protein food”.
Page 211
Question 1. What management practices are common in dairy and poultry farming?
Answer:
- Shelter: Dairy animals and poultry birds require proper shelter, i.e., well designed dairy and hygienic shelter.
- Feeding: To get good yield of food product, proper feed is provided to dairy animals and poultry birds.
- Caring for animal health: Animal and birds must be protected from diseases caused by virus, bacteria or fungi.
Question 2. What are the differences between broilers and layers and in their management?
Answer: The poultry bird groomed for obtaining meat is called broiler. The egg laying poultry bird is called layer.
The housing, nutritional and environmental requirements of broilers are somewhat different from those of egg layers.
The ration (daily food requirement) for broilers is protein rich with adequate fat. The level of vitamins A and K is kept high in the poultry feeds while layers require enough space and proper lightning.
Page 213
Question 1. How are fish obtained?
Answer: There are two ways of obtaining fish. One is from natural resources, which is called capture fishing. The other way is by fish farming, which is called culture fishery.
Question 2. What are the advantages of composite fish culture?
Answer: In composite fish culture, a combination of five or six fish species is used in a single fish pond. These species are selected so that they do not compete for food among them and are having different types of food habits. As a result, the food available in all the parts of the pond is used. For example, Catlas are surface feeders, Rohus feed in the middle-zone of the pond, Mrigals and Common Carps are bottom feeders and Grass Carps feed on the weeds, together these species can use all the food in the pond without competing with each other. This increases the fish yield from pond.
– Page 213
Question 1. What are the desirable characters of bee varieties suitable for honey production?
Answer:
- The variety of bee should be able to collect a large amount of honey.
- The bees should stay in a given beehive for a longer period.
- The bees should have capacity of breeding well.
- The variety of bee should be disease resistant.
Question 2. What is pasturage and how is it related to honey production?
Answer: The pasturage means the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. In addition to adequate quantities of pasturage, the kind of flowers available will determine the taste of the honey.
Question 1. Explain any one method of crop production which ensures high yield.
Answer: One method used for crop production which ensures high yield is plant breeding. It is the science involved in improving the varieties of crops by breeding plants. The plants from different areas/places is picked up with desired traits and then hybridisation or cross-breeding of these varieties is done to obtain a plant/crop of desired characteristic.
The high yielding crop variety shows the following characteristics:
High yield, early maturation, less water for irrigation, better quality seeds are produced, less fertilizers required, adapts itself to the environmental conditions.
Question 2. Why are manure and fertilizers used in fields?
Answer: They are used to ensure good vegetative growth (leaves, branches and flowers), giving rise to healthy plants, that results in high crop production.
Question 3. What are the advantages of inter-cropping and crop rotation?
Answer: Advantages of using inter-cropping:
- It helps to maintain soil fertility.
- It increases productivity per unit area.
- Save labour and time.
- Both crops can be easily harvested and processed separately.
Advantages of using crop rotation:
- It improves the soil fertility.
- It avoids depletion of a particular nutrient from soil.
- It minimise pest infestation and diseases.
- It helps in weed control.
- It prevents change in the chemical nature of the soil.
Question 4. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful in agricultural practices?
Answer: Genetic manipulation is a process of incorporating desirable (genes) characters into crop varieties by hybridisation. Hybridisation involves crossing between genetically dissimilar plants. This is done for production of varieties with desirable characteristics like profuse branching in fodder crops, high yielding varieties in maize, wheat, etc.
Genetic manipulation is useful in developing varieties which shows:
- Increased yield
- Better quality
- Shorter and early maturity period
- Better adaptability to adverse environmental conditions
- Desirable characteristics
Question 5. How do storage grain losses occur?
Answer: The factors responsible for loss of grains during storage are:
- Abiotic factors like moisture (present in foodgrains), humidity (of air) and temperature.
- Biotic factors like insects, rodents, birds, mites and bacteria.
Question 6. How do good animal husbandry practices benefit farmers?
Answer: Good animal husbandry practices are beneficial to the farmers in the following ways:
- Improvement of breeds of the domesticated animals.
- Increasing the yield of foodstuffs such as milk, eggs and meat.
- Proper management of domestic animals in terms of shelter, feeding, care and protection against diseases.
Which ultimately helps the farmers to improve their economic condition.
Question 7. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
Answer: Cattle farming is beneficial in the following ways:
- Milk production is increased by high yielding animals.
- Good quality of meat, fibre and skin can be obtained.
- Good breed of draught animals can be obtained.
Question 8. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and bee-keeping?
Answer: Through cross breeding, the production of poultry, fisheries and bee-keeping can be increased.
Question 9. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture, and aquaculture?
Answer:
Capture fishing: It is the fishing in which fishes are captured from natural resources like pond, sea water and estuaries.
Mariculture: It is the culture of fish in marine water. Varieties like prawns, oysters, bhetki and mullets are cultured for fishing.
Aquaculture: It is done both in fresh water and in marine water.




