EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
18/10/2021 CLASS-10 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT :SCIENCE
chapter - 7
CONTROL AND CO-ORDINATION
______________________________________
Question 1 Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin
Answer:
(d) Cytokinin
Question 2 The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite
(b) synapse
(c) axon
(d) impulse
Answer:
(b) Synapse
Question 3 The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking
(b) regulating the heart beat
(c) balancing the body
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(b) All of the above
Question 4 What is the function of receptors in our body ? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise ? [AICBSE 2016]
Answer:
Receptors are specialised cells located in our sense organs like ear, nose, skin, tongue and eyes. The function of receptors is to detect information from the environment. For example, olfactory receptors detect smell. If receptors do not work properly, the information obtained from the environment will be delayed to reach the spinal cord or brain. In this situation, the response to the environmental stimulus will be delayed causing harm to the body. For example, if skin receptors are damaged, and one accidentally touches a hot object, then his/her hands might get burn as the damaged receptor cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
Question 5 Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function. [AICBSE 2017]
Answer:
Nerve cell or neuron is the functional unit of nervous system. A nerve cell has three parts-
(i) cell body
(ii) dendrite
(iii) axon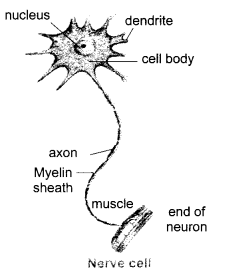
Function : The function of nerve cells is to carry information in the form of electrical signals which are called nerve impulses. Cells receive stimulus to send it to spinal cord and brain and carry the message from brain to the target organ.
Question 6 How does phototropism occur in plants ?
Answer:
The movement in any part of a plant due to light is called phototropism. The shoot of plant shows positive phototropism and roots show negative phototropism.
Phototropism in plants occurs due to the hormone auxin. When light falls on one side of a plant, the secretion of auxin hormone is more in the part away from the light. Hence, auxin causes growth in length of the cells in shady part. So, the plant appears to bend towards light.
Question 7 Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury ?
Answer:
(i) All the involuntary actions will get disturbed.
(ii) Reflex actions will be disturbed because reflexes are located in the spinal cord. Therefore, the quick responses required to safe guard the body will not take place.
Question 8 How does chemical coordination occur in plants ?
Answer:
Chemical coordination in plants takes place with the help of plant hormones. In most of the regions where division takes place (meristematic regions) stimuli cells secrete chemical compounds (hormone). These substances identify the information by stimulating the other nearby cells and communicating the information.
Question 9 What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism ?
Answer:
An organism needs control and coordination system for the following functions :
(i) To save the body of the organisms from the harmful changes in the environment.
(ii) To control the speed of voluntary and involuntary actions.
(iii) To have the capability to think and learn for responding to any stimuli.
Question 10 How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other ?
Answer:
| Involuntary actions | Reflex actions |
| 1. Those actions which occur immediately without any thinking are called involuntary actions. | 1. Reflex action is an immediate response to an event which does not require any processing by brain. |
| 2. Involuntary actions are controlled by mid and hind brain. Example: Breathing, beating of heart, etc. | 2. Reflex actions are controlled by spinal cord. Example: Sneezing, coughing, etc. |
Question 11 Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
| Nervous mechanism | Hormonal mechanism |
| It is a fast process. | It is a slow process. |
| Arteries and glands are affected. | It affects the target organ. |
| It transmits in electrochemical form. | It transmits in chemical form. |
| It does not control metabolism. | It controls metabolism. |
| Growth is not affected. | Growth is affected. |
Question 12 What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs ?
Answer:
| Movement in a sensitive (mimosa) plant | Movement in legs of a human |
| 1. The leaves of a sensitive plant like mimosa are sensitive to touch. | 1. Leg is in control of nerve muscles. |
| 2. It is not controlled by any part of the plant. | 2. It is controlled by brain and spinal cord. |
| 3. In this, cells change their shape on changing the amount of water in them. | 3. Amount of water has no effect on the movement of muscles. |
| changing the amount of water in them. | the movement of muscles. |
| 4. The movement in a sensitive plant are nastic movement. | 4. The movement in our leg is due to voluntary nervous system. |
Control and Coordination Class 10 HOTS
Question 1. What type of plant movement is seen in the diagram of coiling of tendril?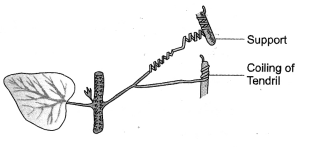
Or
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support? Describe in brief. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Thigmotropism or curvature movement that occurs in response to contact. Less auxin is present in the region of contact. The free side having more auxin shows more growth. This causes the tendril to coil over the support.
Question 2. Identify and label the parts shown as A and B in the accompanying figure.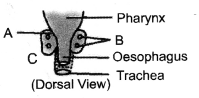
Answer:
Dorsal view of thyroid an parathyroid.
A – Thyroid,
B- Parathyroid.
Question 3. What are the hormones involved in providing milk to the suckling infant ?
Answer:
1. Prolactin (Maternity Hormone). Production of milk.
2. Oxytocin Ejection of milk.
Question 4. How does pancreas control glucose level of blood ?
Answer:
Pancreas produces two hormones
- Insulin from P-cells of islet of Langerhans and
- Glucagon from a- cells of islets of langerhans.
Insulin is produced when glucose level of blood rises. Insulin helps the cells to withdraw glucose from blood. It also converts glucose into glycogen in liver and muscles.
Question 5. Glucagon is secreted when glucose level of blood falls. It mobilises reserve food like glycogen into glucose. What is pregnancy hormone ? Why is it known so ?
Answer:
Progesterone is called pregnancy hormone. It helps in maintaining pregnancy by non-formation of new ova, promoting thickening and secretory activity of uterine wall and attachment of embryo to the uterine wall.
Question 6. What is dormin ?
Answer:
Dormin is the other name of plant hormone abscisic acid. The hormne induces dormancy in buds and seeds. So it has been called dormin.
Question 7. Name the parts labelled A and B in the neuron drawn above.
- Which part acquires the information in the neuron ?
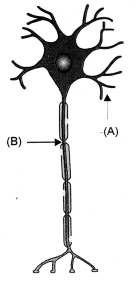
- Through which part does the information travel ?
- In what form does this information travel ?
- Where is the impulse converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission ?
(b) Name the hormone secreted by thyroid. What is the function ?
(c) Why is the use of iodised salt advisable ?
(CBSE A.I. 2008 Compt.)
Answer:
(a)
- A-Dendrite, B-Axon
- Dandrite.
- Dandrite to cell body or cyton to axon.
- Electrical impulse
- In the region of synapse.
Impulse stimulates the release of chemical neurotransmitter from the surface of presynaptic knob or bouton of axon terminal. Neurotransmitter (e.g. acetylcholine) comes in contact with chemoreceptor sites of post-synaptic membrane of the next neuron and generates a fresh impulse.
(b) Thyroxine:
Function of Thyroxine. It controls
- Basal metabolic rate
- Metabalism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
- Consumption of energy in physical activity and body temperature
- Development and differentiation.
(c) Iodised Salt: Salt is iodised to provide iodine to thyroid for synthesis of thyroxine which is iodine containing hormone.
Question 8.
(a) What are plant hormones ? Give one example each of a plant hormone that
- promotes growth
- inhibits growth.
- promotes cell division
- promotes the growth of a tendril around a support. (CCE 2011)
(b) Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram given below. Write one function of each part. (CBSE A.I. 2008 Comptt. Delhi 2008 Comptt.)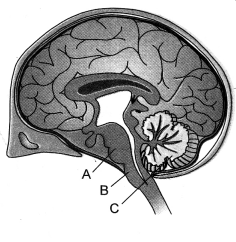
Answer:
(a) Plant Hormones:
Phytohormones are chemical substances other than nutrients produced naturally in plants which regulate growth, development, differentiation and a number of physiological processes, e.g., auxin, gibberellins, abscisic acid, cytokinins.
- Hormone That Promotes Growth. Auxin/Gibberellin.
- Hormone That Inhibits Growth. Abscisic acid or ABA
- Hormone That Promotes Cell Division. Cytokinin.
- Hormone That Promotes Growth of a Tendril Around a Support. Auxin.
(b) A-Pons Function: Relay centre, pneumotaxic area of respiratory centre.
B-Medulla Function: Reflex centre, cardiac centre, respiratory centre.
C-Cerebellum Function: Maintains equilibrium and coordinates muscular activities

