EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
08/01/2022 CLASS- 9 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT :SCIENCE HINDI MEDIUM
CHAPTER-4
STRUCTURE OF ATOM
______________________________________
(Hindi Medium)










EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL


















EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
Textbook – Page 47
Question 1. What are canal rays?
Answer: Canal rays are positively charged radiations which led to the discovery of positively charged sub-atomic particle called proton.
Question 2. If an atom contains one electron and one proton, will it carry any charge or not?
Answer: The atom will be electrically neutral as one – ve charge balances one + ve charge.
Textbook – Page 49
Question 1. On the basis of Thomson’s model of an atom, explain how the atom is neutral as a whole.
Answer: According to Thomson’s model of an atom
(i) An atom consists of a positively charged sphere and the electrons are embedded in it,
(ii) The negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude. So the atom is electrically neutral.
Question 2. On the basis of Rutherford’s model of an atom, which sub-atomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
Answer: As per Rutherford’s model of an atom, the protons which are positively charged are present in the nucleus of an atom.
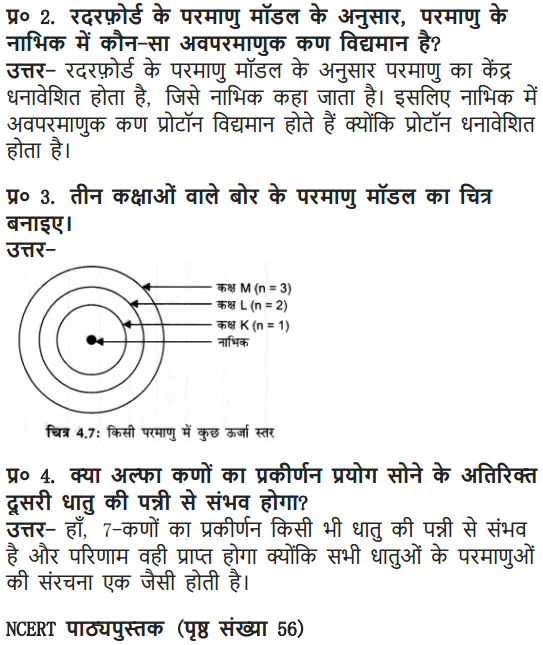
Question 3. Draw a sketch of Bohr’s model of an atom with three shells.
Answer: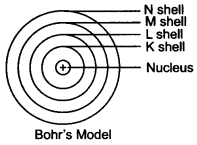
Question 4. What do you think would be the observation if the a-particle scattering experiment is carried out using a foil of a metal other than gold?
Answer: On using any metal foil, the observations of the a-particle scattering experiment would remain the same as all atoms would have same structure.
Textbook – Page 49
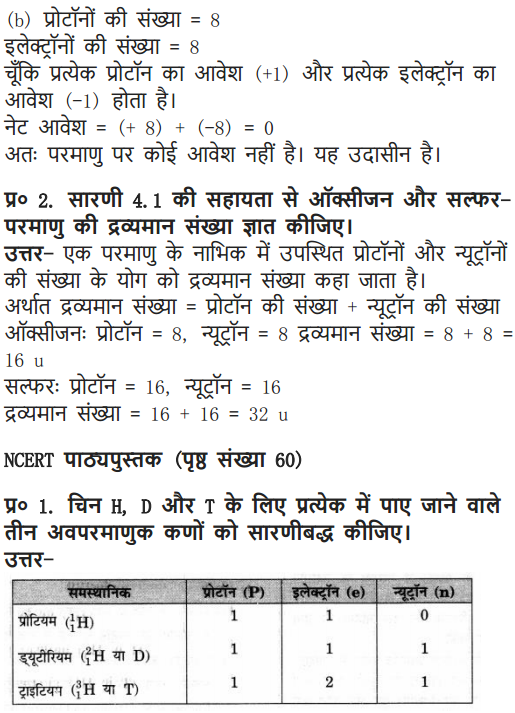
Question 1. Name the three sub-atomic particles of an atom.
Answer: The sub-atomic particles of an atom are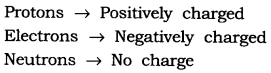
Question 2. Helium atom has an atomic mass of 4 u and two protons in its nucleus. How many neutrons does it have?
Answer: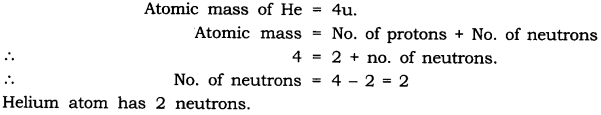
Textbook – Page 50
Question 1. Write the distribution of electrons in carbon and sodium atoms.
Answer:
Question 2. If K and L shells of an atom are full, then what would be the total number of electrons in the atom?
Answer: K shell can hold 2 electrons and L shell can hold 8 electrons.When both the shells are full, there will be (8 + 2) 10 electrons in the atom.
Text Book
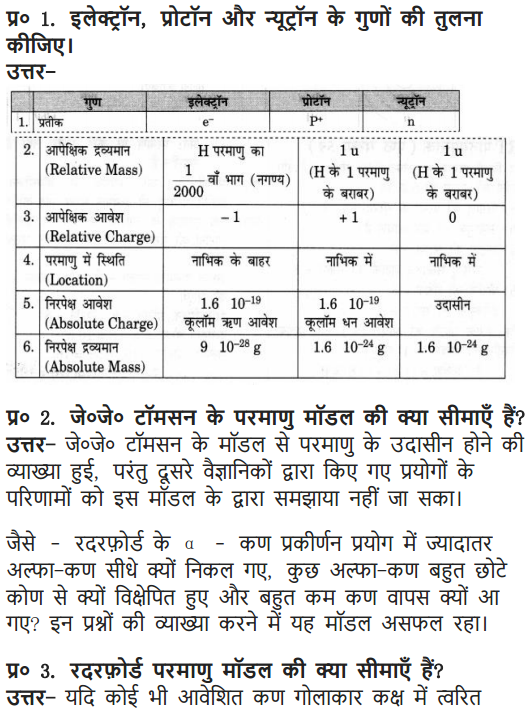
Question 1. Compare the properties of electrons, protons and neutrons.
Answer: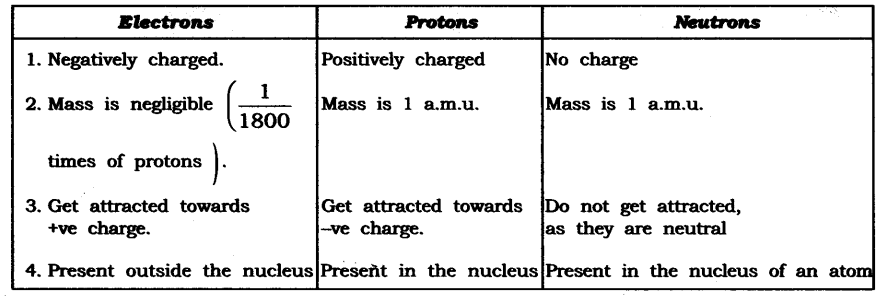
Question 2. What are the limitations of J.J. Thomson’s model of the atom?
Answer: According to J.J. Thomson’s model of an atom, the electrons are embedded all over in the positively charged spheres. But experiments done by other scientists showed that protons are present only in the centre of the atom and electrons are distributed around it.
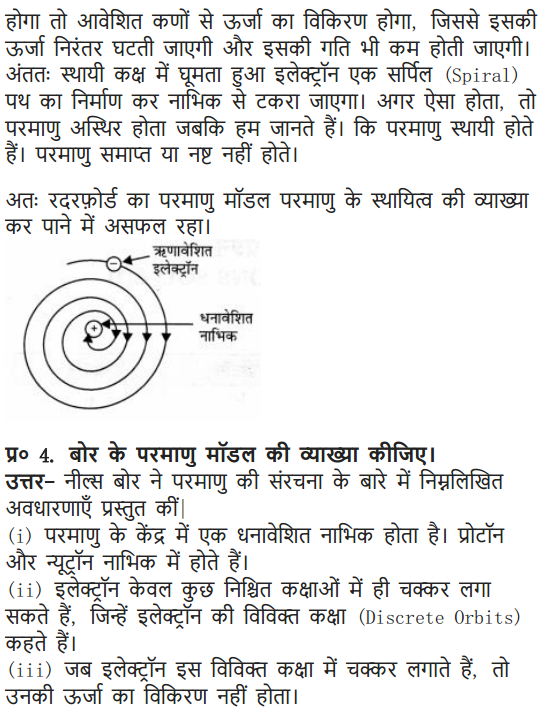
Question 3. What are the limitations of Rutherford’s model of the atom?
Answer: According to Rutherford’s model of an atom the electrons are revolving in a circular orbit around the nucleus. Any such particle that revolves would undergo acceleration and radiate energy. The revolving electron would lose its energy and finally fall into the nucleus, the atom would be highly unstable. But we know that atoms are quite stable.
Question 4. Describe Bohr’s model of the atom.
Answer: Bohr’s model of the atom
(1) Atom has nucleus in the centre.
(2) Electrons revolve around the nucleus.
(3) Certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons are allowed inside the atom.
(4) While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy.
(5) These orbits or shells are called energy levels.
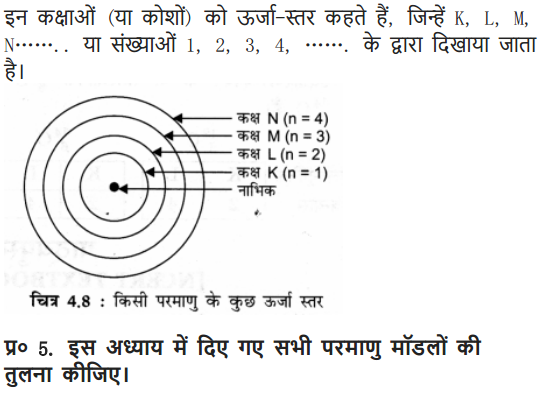
(6) These orbits or shells are represented by the letters K, L, M, N or the numbers n = 1, 2, 3, 4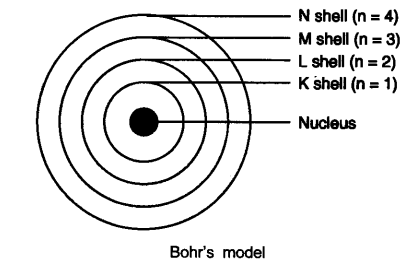
Question 5. Compare all the proposed Bohr’s models of an atom given in this chapter.
Answer: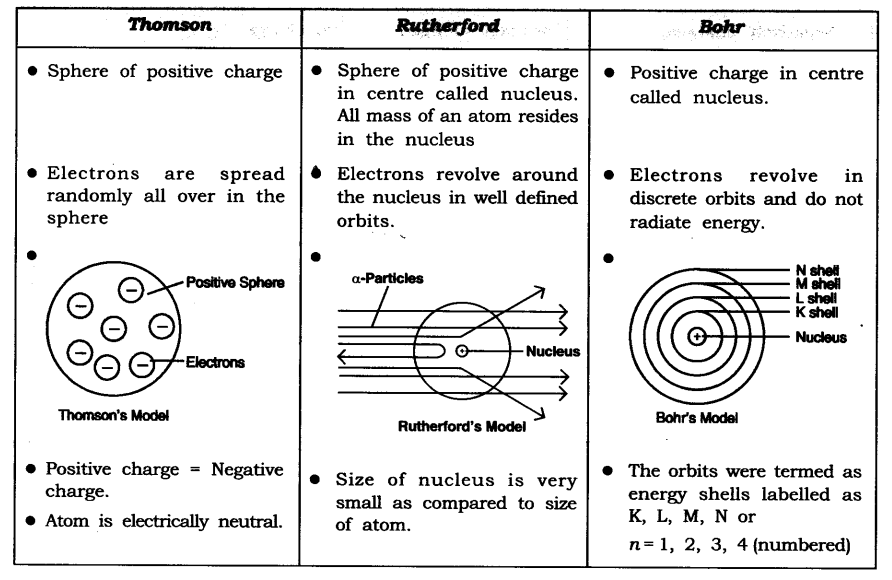
Question 6. For the following statements, write T for True and F for False.
(a) J.J. Thomson proposed that the nucleus of an atom contains only nucleons.
(b) A neutron is formed by an electron and a proton combining together. Therefore,it is neutral.
(c) The mass of an electron is about 1/2000 times that of proton.
(d) An isotope of iodine is used for making tincture iodine, which is used as a medicine.
Answer: (a) False (b) False
(c) True (d) False
Question 7. Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment was responsible for the discovery of
(a) Atomic nucleus (c) Proton
(b)Electron (d)neutron
Answer: (a) Atomic nucleus
Question 8.Isotopes of an element have
(a) the same physical properties (c) different number of neutrons
(b)different number of neutrons (d) different atomic numbers.
Answer: (c) different number of neutrons
Question 9. Number of valence electrons in Ct ion are :
(a) 16 (b) 8
(c) 17 (d) 18
Answer: (b) 8
Question 10. Which one of the following is a correct electronic configuration of sodium?
(a) 2, 8 (b) 8, 2, 1
(c) 2, 1, 8 (d) 2, 8, 1
Answer: (d) 2, 8, 1
Question 11. Complete the following table.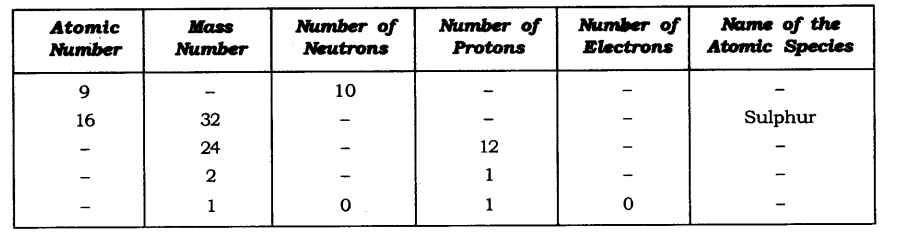
Answer: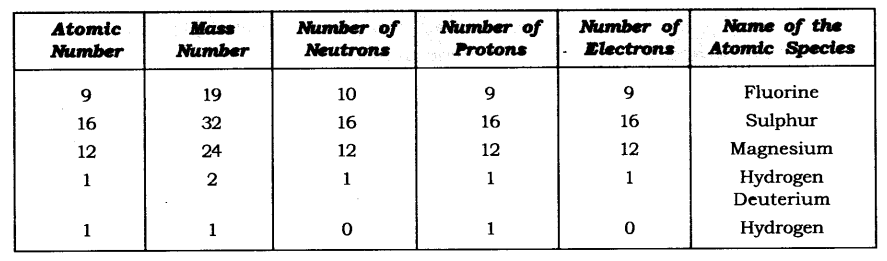
EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
Q.1. Classify the following fibres as natural or synthetic: nylon, wool, cotton, silk, polyester, jute.
Ans. Natural fibres: wool, cotton, jute, silk.
Synthetic fibres: nylon, polyester.
Q.2. State whether the following statements are ‘true’ or false’:
(a) Yam is made from fibres.
(b) Spinning is a process of making fibres.
(c) Jute is the outer covering of coconut.
(d) The process of removing seeds from cotton is called ginning.
(d) Weaving of yam makes a piece of fabric.
(e) Silk fibre is obtained from the stem of a plant.
(g) Polyester is a natural fibre.
Ans.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) False
(d) True
(e) True
(f) False
(g) False
Q.3. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Plant fibres are obtained from____________ and___________ .
(b) Animal fibres are___________ and___________ .
Ans.
(a) cotton plants, jute plants
(b) wool, silk
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Name two varieties of cloth materials which are commonly used.
Ans. Cotton, silk/wool.
Q.2. What are fabrics?
Ans. Fabrics mean a woven material, textile or other materials resembling woven cloth.
Q.3. Name some fabrics in your surroundings.
Ans. Bed-sheets, blankets, curtains, table clothes, towels and dusters.
Q. 4. Name the thing which is used to make fabric.
Ans. Yarns.
Q.5. What are yarns made of?
Ans. Yarns are made up of thin strands called fibres.
Q.6. How many types of fibres are there? ,
Ans. There are two types of fibres:
(i) Natural fibres
(ii) Synthetic fibres
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. What do you observe when you are visiting a nearby tailoring shop?
Ans. In a tailoring shop we observe that there are many cuttings of fabrics left over after stitching. We see that some cuttings are of cotton, some are of silk or wool and some are of synthetic fibres.
Q.2. List the steps involved in the preparation of fabric.
Ans. The following steps are involved in the preparation of fabrics:
(i) Obtaining fibre,
(ii) Preparation of yarn from fibres by spinning,
(iii) When two sets of yarn are involved, yarns are woven on looms to make a fabric. When a single yam is used, the fabric is prepared by knitting.
Q.3. What are natural fibres? Explain with examples.
Ans. The fibres obtained from plants and animals are called natural fibres. For example, cotton from cotton bolls, jute from jute plant, silk from cocoon of silkworm and wool from hair of animals like sheep or goat.
Q.4. What are synthetic fibres?
Ans. The fibres which are made from chemical substances or which are not obtained from the plant and animal sources are called synthetic fibres. For example, polyester, nylon, and acrylic, etc.
Q.5. Explain how jute is obtained from the jute plant.
Ans. The jute plant is normally harvested at flowering stage. The stems of harvested plants are bundled and immersed in water for 10 to 15 days. The stems rot (the process is called retting) and fibres are separated by hand. These fibres are converted into yarns to make fabrics (Fig. 3.10).
Q. 6. What are looms?
Ans. The devices on which weaving of fabrics takes place are called looms. The looms are either hand operated or power operated.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Describe the process of the formation of yam from cotton wool.
Ans. The cotton wool is obtained from cotton plants. The cotton plants are grown in fields. They are usually grown at the places having black soil and warm climate. The fmits of the cotton plants called cotton bolls are about the size of lemons. After maturing, the bolls burst open and seeds covered with cotton fibres can b,e seen. From the cotton bolls cotton is picked by hands. Fibres are then separated from the seeds by combing. This process is called ginning of cotton. It is done by hand or by machines. These fibres are then converted into yam.
Q.2. Describe the process of spinning and weaving.
Ans. Spinning: The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning. In this process fibres from a mass of cotton wool are drawn out and twisted. By this fibres come together to form a yarn. Spinning can be done by hand, by takli and charkha. On a large scale, spinning is done with the help of machines.
Weaving: The process of arranging two sets of yarns together t6 make a fabric is called weaving. The process of weaving can be done on looms. The looms are either-hand operated or power operated.