EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
25/01/2022 CLASS- 6 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT :MATHS
CHAPTER-12
______________________________________
Exercise 12.2
Question 1.Determine if the following are in proportion,
(a) 15, 45, 40, 120
(b) 33, 121, 9, 96
(c) 24, 28, 36, 48
(d) 32, 48, 70, 210
(e) 4, 6, 8, 12
(f) 33, 44, 75, 100
Solution: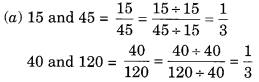
∴ 15 : 45 :: 40 : 120
∴ 15, 45, 40 and 120 are in proportion.
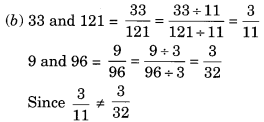
∴ 33, 121, 9 and 96 are in proportion.
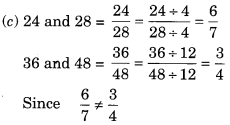
∴ 24, 28, 36 and 48 are not in proportion.
Question 2 Determine if the following ratios form a proportion. Also, write the middle terms and extreme terms where the ratios form a proportion.
(a) 25 cm : 1 m and ₹ 40 : ₹ 160
(b) 39 litres : 65 litres and 6 bottles : 10 bottles
(c) 2 kg : 80 kg and 25 g : 625 g
Solution:
(a) 25 cm : 1 m = 25 cm : 100 cm [∵ 1 m = 100 cm]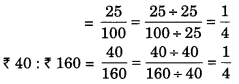
∴ The given ratios are in proportion.
Extreme terms are 25 cm and ₹ 160.
Middle terms are 1 m and ₹40.
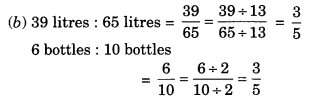
∴ The given ratios are in proportion.
Extreme terms are 39 litres and 10 bottles.
Middle terms are 65 litres and 6 bottles.
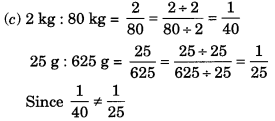
∴ The given ratios are not in proportion.
Question 3. Are the following statements true?
(a) 40 persons : 200 persons = ₹15 : ₹75
(b) 7.5 litres : 15 litres = 5 kg : 10 kg
(c) 99 kg : 45 kg = ₹ 44 : ₹ 20
Solution:
(a) 40 persons : 200 persons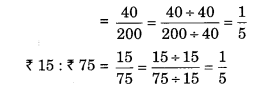
∴ Statement (a) is true.
(b) 7.5 litres : 15 litres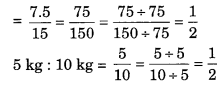
∴ Statement (b) is true.
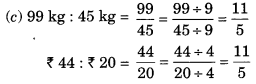
∴ Statement (c) is true.