EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
30/10/2021 CLASS- 6 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT : SCIENCE
CHAPTER-12
ELECTRICITY & CIRCUITS
______________________________________
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called_______________
(b) An electric cell has___________
Ans:
(a) switch
(b) two
2. Mark ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the following statements:
(a) Electric current can flow through metals.
(b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
(c) Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol.
Ans:
(a) True
(b) False
(c) False.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is the direction of flow of current in a dry cell?
Ans: . The current flows in closed circuit from +ve to -ve terminal of cell.
2. Name the +ve terminal of dry cell.
Ans:. Carbon rod with a metal cap on it.
3. Name the -ve terminal of a dry cell.
Ans: Zinc metal plate.
4. What is dry cell?
Ans: It is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
5. What is solar cell?
Ans: A device which converts solar energy into electrical energy.
6. What is open circuit?
Ans: An electric circuit in which electrical contact at any point is broken is called open circuit.
7. Write one use of insulators.
Ans: Insulators are used in making switchboard, handles of testers, screw drivers.
8. What is the name of thin wire in the electric bulb?
Ans: Filament.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Mention two advantages of a dry cell.
Ans:
1. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
2. It is light and small in size.
2. Draw a diagram showing the two terminals of a bulb.
Ans: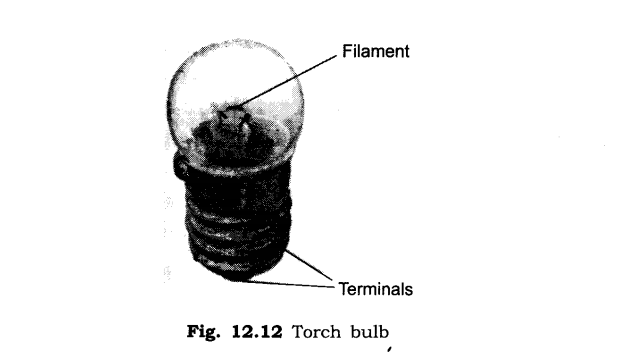
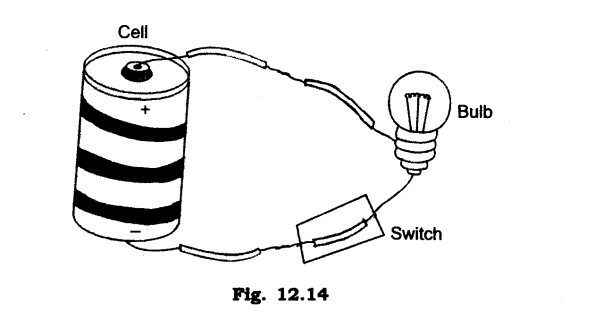
3. Draw the circuit diagram for operating a bulb with the help of a dry cell.
Ans: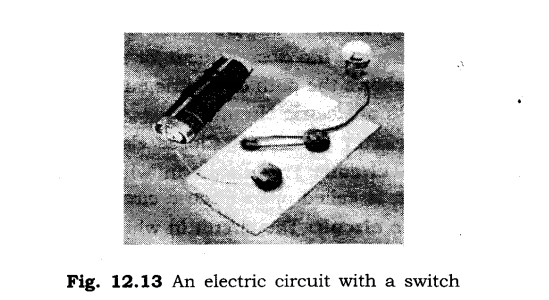
4. Define conductors and insulators. Give one example of each.
Ans: A conductor is that which easily allows the passage of current through it. Example: Aluminium or any metal.
An insulator is that which does not allow the passage of current through it. Example: Rubber.
5. Identify conductors and insulators from the following:Eraser, paper, matchstick, copper wire, pencil lead, polythene
Ans: Conductors: Copper wire, pencil lead.
Insulator. Eraser, paper, matchstick, polythene.
6. Name the scientist who invented electric cell and the scientist who invented electric bulb.
Ans: Electric cell: Alessandro Volta.
Electric bulb: Thomas Alva Edison.
7. Give one activity to prove that air is an insulator.
Ans: Take an electric circuit, keep the terminals unconnected in the air. The bulb do not glow, as air is an insulator and does not allow the current to flow through it.
8. In any electric circuit, when the switch is on and the current flows through it why do the wire, switches, bulb or devices become hot?
Ans.: This is because electric energy changes into heat energy.
9.The headlights of a car have reflectors behind the bulb. What is the function of reflectors?
Ans: The reflector helps in reflecting the light into a focussed area.
10.If you touch an electric wire carrying current you get a shock, but if on the same wire the birds sit they do not get any shock/current. Explain why?
Ans: When we hold the wire carrying current then the circuit is closed and the current flows from our body and enters earth but the birds sitting on the same wire do not get any current as the circuit is not complete. If the bird touches the earth wire, it will also die due to electric shock.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.(1)What is electric circuit?
(2)How many types of electric circuit are there? Define them.
(3)Draw a diagram to show the closed circuit for switch, bulb and dry cell.
Ans:
(1)The diagram that shows the path of electric current is called electric circuit.
(2)There are two types of electric circuit:
(a) Open electric circuit
(b) Closed electric circuit
(a)Open electric circuit: The circuit in which electrical contact at any point is broken is called open electric circuit.
(b)Closed electric circuit: The circuit in which electric current flows from one terminal of a cell or battery to the other is called a closed circuit.