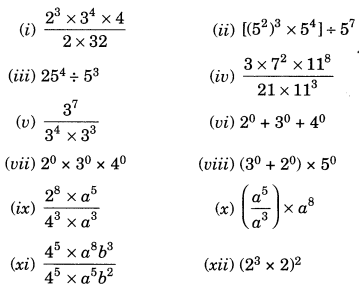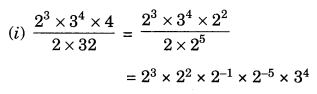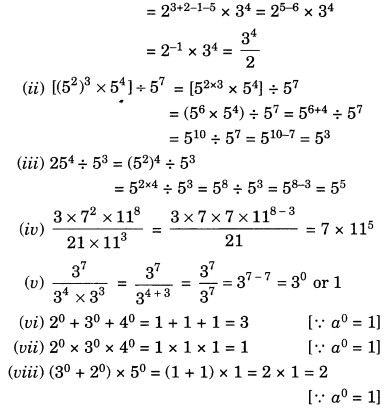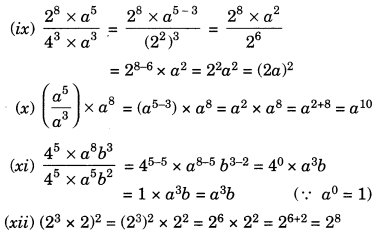EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
27/01/2022 CLASS- 9 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE
CHAPTER-5
NATURAL VEGITATION AND WILDLIFE
______________________________________
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.The number of flowering plants in India is about _______ .
Answer:
15,000
Question 2.Name two non-flowering plants.
Answer:
Algae, fungi and ferns.
Question 3.The sandy soils of desert support _______ .
Answer:
Cactus and thorny bushes.
Question 4.Sundari trees are found in _______ .
Answer:
Tidal Forests
Question 5.A very large ecosystem on land having distinct type of vegetation and animal life is called _______ .
Answer:
Biome
Question 6.At higher altitudes, mosses and lichens form part of _______ .
Answer:
Tundra vegetation
Question 7.The dry deciduous forests are found in areas having rainfall between _______ .
Answer:
100 cm and 70 cm
Question 8.The mangrove tidal forests are found in the areas of coasts influenced by sea _______ .
Answer:
Tides
Question 9.Royal Bengal Tiger is found in _______ .
Answer:
Mangrove forests
Question 10.Wildlife Protection Act was implemented in India in _______ .
Answer:
1972
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.How do human beings influence the ecology of a region?
Answer:
Human beings influence the ecology of a region in the following ways :
- They utilise the vegetation and wildlife of a particular region.
- The greed of human beings leads to overutilisation of these resources.
- They cut trees and kill the animals, thereby, creating an ecological imbalance.
Question 2.What are endangered species? Give examples.
Answer:
- The plants and animals that are at the verge of extinction are called endangered species.
- Rhinoceroes, Great Indians bustards and tigers are some of the examples of endangered species of animals.
Question 3.Write a short note on the biodiversity in India.
Or
‘India is one of the 12 mega biodiversity countries of the world’. Explain
Answer:Our country India is one of the 12 mega bio-diversity countries of the worid. With about 47,000 plant species, India occupies tenth place in the world and fourth in Asia in plant diversity.
- There are about 15,000 flowering plants in India, which account for 6 per cent in the world’s total number of flowering plants.
- The country has many non-flowering plants, such as ferns,’algae and fungi. India also has 90,000 species of animals, as well as, a rich variety of fish in its fresh and marine waters.
Question 4.Discuss how flora and fauna are interrelated to each other.
Answer:
The interrelation between flora and fauna is as under :
- Flora refers to the autotrophs, i.e., producer of their own food themselves, while fauna refers to the heterotrophs, i.e., getting their food directly or indirectly from autotrophs.
- Food webs and food chains make ex-facie the interrelation between the flora and fauna.
- Flora provides food to all living organisms while fauna provides nutrients to the soil from its waste and decay.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1 Distinguish between the moist and dry deciduous forests.
Answer:
| Moist Deciduous Forests | Dry Deciduous Forests |
| 1. These are found in areas receiving annual rainfall between 100 cm and 200 cm. | 1. These forests are found in areas receiving annual rainfall between 70 cm and 100 cm. |
| 2. Trees found in these forests are teak, sal, shisham, sandalwood, khair and bamboos. | 2. There are open stretches in which, teak, sal, peepal, neem, etc. grow. |
| 3. These forests are generally found in Jharkhand, West Odisha, Chhattisgarh and on the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. | 3. These forests are found in the rainer parts of the peninsular plateau and the plains of U.R, and Bihar. |
Question 2 Write a short note on thorny forests and scrubs.
Answer:
The thorny forest and scrubs are found in regions with less than 70 cm of rainfall, the natural vegetation consists of thorny trees and bushes. This type of vegetation is found in the north-western part of the country, including semi-arid areas of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana. Acacias, palms, euphorbias and cacti are the main plant species. Trees are scattered and have long roots penetrating deep into the soil to get moisture. The stems are succulent to conserve water. Leaves are mostly thick and small to minimise evaporation. These forests give way to thorn forests and scrubs in arid areas. In these forests, the common animals are rats, mice, rabbits, fox, wolf, tiger, lion, wild ass, horses and camels.
Question .3 Write three measures to conserve ecosystem.
Answer:
The measures to conserve ecosystem are :
- Deforestation has disturbed our ecosystem. It must be stopped forthwith.
- Indiscriminate killing of wild animals has distorted our ecosystem. Hence, killing of
animals should be stopped immediately. - Ecosystem can be conserved by developing more wildlife sanctuaries, national parks and biosphere reserves.
Question. 4Why is conservation of wildlife very essential? Explain.
Answer:
The government has taken many special efforts to preserve endangered species of birds and animals. Periodic census is undertaken to find out the latest position and trends in this regard. The Project Tiger has been a great success. We have many tiger reserves in various parts of the country. Likewise, the Project Rhino is being implemented in Assam. The Indian Bustard of Rajasthan and Malwa Plateau are yet another endangered species. Even the number of lions had been dwindling for long. Conservation of wildlife is essential in order to protect the endangered species of birds and animals and also to maintain the ecological balance. The Government of India has so far set-up eighteen biosphere reserves.