EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
27/11/2021 CLASS- 7 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE GEOGRAPHY
CHAPTER-9
LIFE IN DESERT
______________________________________
1. Answer the following questions briefly:
(a) What are the two types of deserts found in the world?
(b) In which continent is the Sahara desert located?
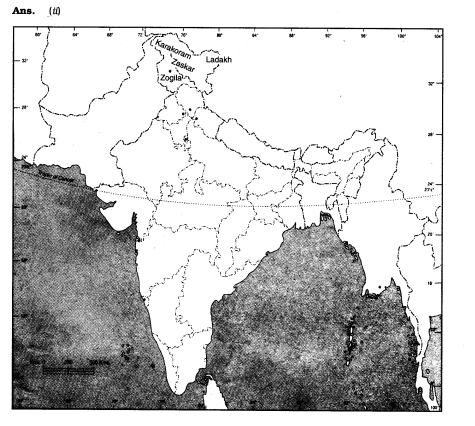
(c) What are the climatic conditions of the Ladakh desert?
(d) What mainly attracts tourists to Ladakh?
(e) What type of clothes the people of the Sahara desert wear?
(f) Name the trees that grow in Ladakh
Answer:
(a) The two types of deserts found in the world are hot deserts and cold deserts.
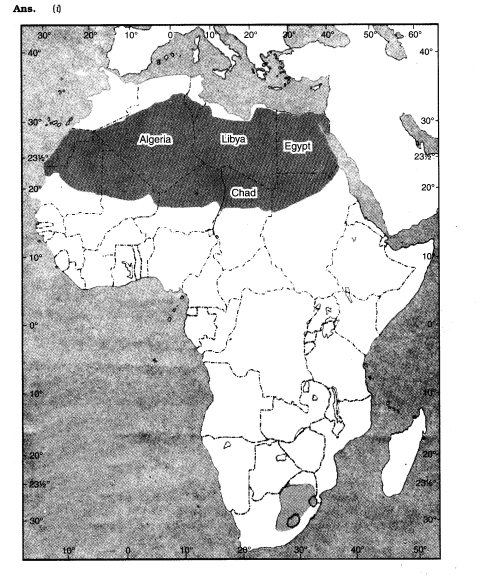
(b) The Sahara desert is located in Africa.
(c) The climate of the Ladakh desert is extremely cold and dry due to its high attitude which varies from about 3,000 m in Kargil to more than 8,000 m in the Karakoram. The air at this attitude is so then that the heat of the sun can be felt intensely. The day temperatures in summer are just above zero degree and the night temperatures are below -30°C. Winters are extremely cold with temperatures below -40°C for most of the time. There is very little rainfall in this region. It is as low as 10 cm every year. The area experiences freezing winds and burning hot sunlight. There is always a chance of sunstroke and frostbite at the same time.
(d) Ladakh is a famous tourist place. The tourists from within the country and abroad enjoy visiting Buddhist monasteries that dot the Ladakhi landscape with their traditional gompas.
The meadows and glaciers in Ladakh also attract these tourists. The ceremonies and festivities in which the local people keep themselves engaged during winter months are great attractions to the tourists.
(e) The people of the Sahara desert wear heavy clothes.
(f) Scanty patches of grasses and shrubs, groves of willows and poplars, fruit trees such as apples, apricots and walnuts.
2. Tick the correct answer:
(i) Sahara is located in which part of Africa?
(a) eastern (b) northern (c) western.
(ii) Sahara is what type of dessert?
(a) cold (b) hot (c) mild.
(iii) The Ladakh desert is mainly inhabited by ………..
(a) Christians and Muslims
(b) Buddhists and Muslims
(c) Christians and Buddhists.
(iv) Deserts are characterized by ……………..
(a) Scanty vegetation (b)heavy precipitation (iii) low evaporation.
(v) Hemis in Ladakh is famous ………………
(a) temple (b) church (c) monastery.
(vi) Egypt is famous for growing
(a) wheat (b) maize (c) cotton.
Answer: (i)-(b), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(a), (v)-(c), (vi)—(c).
3. Match the following:

4. Give reasons:
- There is scanty vegetation in the deserts.
- People of the Sahara desert wear heavy robes.
Answer:
- There is scanty vegetation in the deserts because of the following reasons:
- Vegetation depends on two factors: climate and soil.
- The climate in the deserts is either very hot and dry or very cold and dry.
★ Such a climate does not allow the growth of vegetation.
★ Rainfall is scanty. Hence vegetation does not grow in dry conditions. - Soil is either sandy (in hot deserts) or covered with snow (cold deserts) for most of the year. Both types of soil do not encourage vegetation to grow.
- The climate in the deserts is either very hot and dry or very cold and dry.
- Vegetation depends on two factors: climate and soil.
- People of the Sahara Desert wear heavy robes because of the following reasons:
- Robes of the people of Sahara Desert are made of hides (of animals) or hair of animals.
- These robes are heavy:
- They protect the people from the scorching sun and extreme heat (dust storms and hot winds).
- They protect the people from dust storms and hot winds.
5. Map skills:
(i) On the outline map of Africa, marks the Sahara desert and any four countries around it.
(ii) On the outline map of India, mark the Karakoram Range, Zanskar Range, Ladakh and zojila pass.
Answer: