EVENTS CONVENT HIGH SCHOOL
31/01/2022 CLASS- 9 SESSION 2021-22
SUBJECT : MATHS
CHAPTER-8(eXERCISE 8.1)
QUADRILATERALS
______________________________________
Question 1.The angles of quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 9 : 13. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral.
Solution:
Let the angles of the quadrilateral be 3x, 5x, 9x and 13x.
∴ 3x + 5x + 9x + 13x = 360°
[Angle sum property of a quadrilateral]
⇒ 30x = 360°
⇒ x =
∴ 3x = 3 x 12° = 36°
5x = 5 x 12° = 60°
9x = 9 x 12° = 108°
13a = 13 x 12° = 156°
⇒ The required angles of the quadrilateral are 36°, 60°, 108° and 156°.
Question 2.If the diagonals of a parallelogram are equal, then show that it is a rectangle.
Solution:
Let ABCD is a parallelogram such that AC = BD.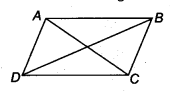
In ∆ABC and ∆DCB,
AC = DB [Given]
AB = DC [Opposite sides of a parallelogram]
BC = CB [Common]
∴ ∆ABC ≅ ∆DCB [By SSS congruency]
⇒ ∠ABC = ∠DCB [By C.P.C.T.] …(1)
Now, AB || DC and BC is a transversal. [ ∵ ABCD is a parallelogram]
∴ ∠ABC + ∠DCB = 180° … (2) [Co-interior angles]
From (1) and (2), we have
∠ABC = ∠DCB = 90°
i.e., ABCD is a parallelogram having an angle equal to 90°.
∴ ABCD is a rectangle.
Question 3.Show that if the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles, then it is a rhombus.
Solution:
Let ABCD be a quadrilateral such that the diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at right angles at O.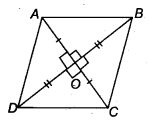
∴ In ∆AOB and ∆AOD, we have
AO = AO [Common]
OB = OD [O is the mid-point of BD]
∠AOB = ∠AOD [Each 90]
∴ ∆AQB ≅ ∆AOD [By,SAS congruency
∴ AB = AD [By C.P.C.T.] ……..(1)
Similarly, AB = BC .. .(2)
BC = CD …..(3)
CD = DA ……(4)
∴ From (1), (2), (3) and (4), we have
AB = BC = CD = DA
Thus, the quadrilateral ABCD is a rhombus.
Alternatively : ABCD can be proved first a parallelogram then proving one pair of adjacent sides equal will result in rhombus.
Question 4.Show that the diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
Solution:
Let ABCD be a square such that its diagonals AC and BD intersect at O.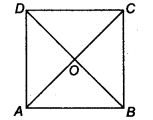
(i) To prove that the diagonals are equal, we need to prove AC = BD.
In ∆ABC and ∆BAD, we have
AB = BA [Common]
BC = AD [Sides of a square ABCD]
∠ABC = ∠BAD [Each angle is 90°]
∴ ∆ABC ≅ ∆BAD [By SAS congruency]
AC = BD [By C.P.C.T.] …(1)
(ii) AD || BC and AC is a transversal. [∵ A square is a parallelogram]
∴ ∠1 = ∠3
[Alternate interior angles are equal]
Similarly, ∠2 = ∠4
Now, in ∆OAD and ∆OCB, we have
AD = CB [Sides of a square ABCD]
∠1 = ∠3 [Proved]
∠2 = ∠4 [Proved]
∴ ∆OAD ≅ ∆OCB [By ASA congruency]
⇒ OA = OC and OD = OB [By C.P.C.T.]
i.e., the diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at O. …….(2)
(iii) In ∆OBA and ∆ODA, we have
OB = OD [Proved]
BA = DA [Sides of a square ABCD]
OA = OA [Common]
∴ ∆OBA ≅ ∆ODA [By SSS congruency]
⇒ ∠AOB = ∠AOD [By C.P.C.T.] …(3)
∵ ∠AOB and ∠AOD form a linear pair.
∴∠AOB + ∠AOD = 180°
∴∠AOB = ∠AOD = 90° [By(3)]
⇒ AC ⊥ BD …(4)
From (1), (2) and (4), we get AC and BD are equal and bisect each other at right angles.